Implementation and Applications
Part 5
7. Implementation
When implementing a neural network, we first need to decide its structure, which determines how the network will
carry out information processing. This includes the number of layers, the number of neurons within each layer, the
types of connections (fully connected, convolutional, recurrent, or attention-based), and the choice of activation
functions like the ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit)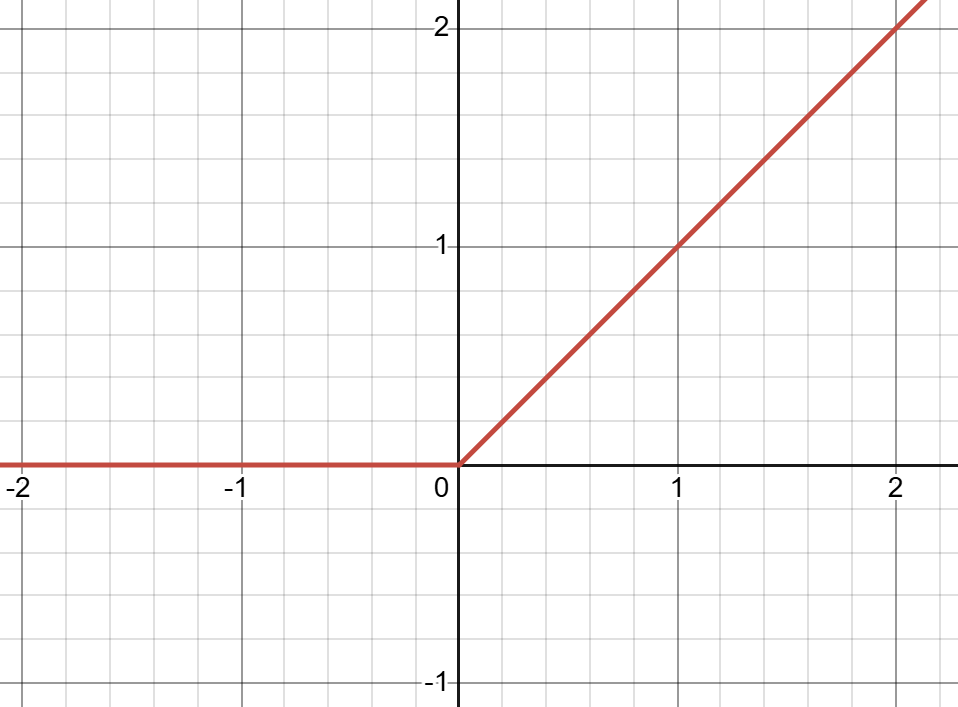
(H.Y. using Desmos)
Equation: \(f(x)=\begin{cases}0 \text{ if } x \leq 0 \\ x \text{ if } x > 0 \end{cases}\)
, sigmoid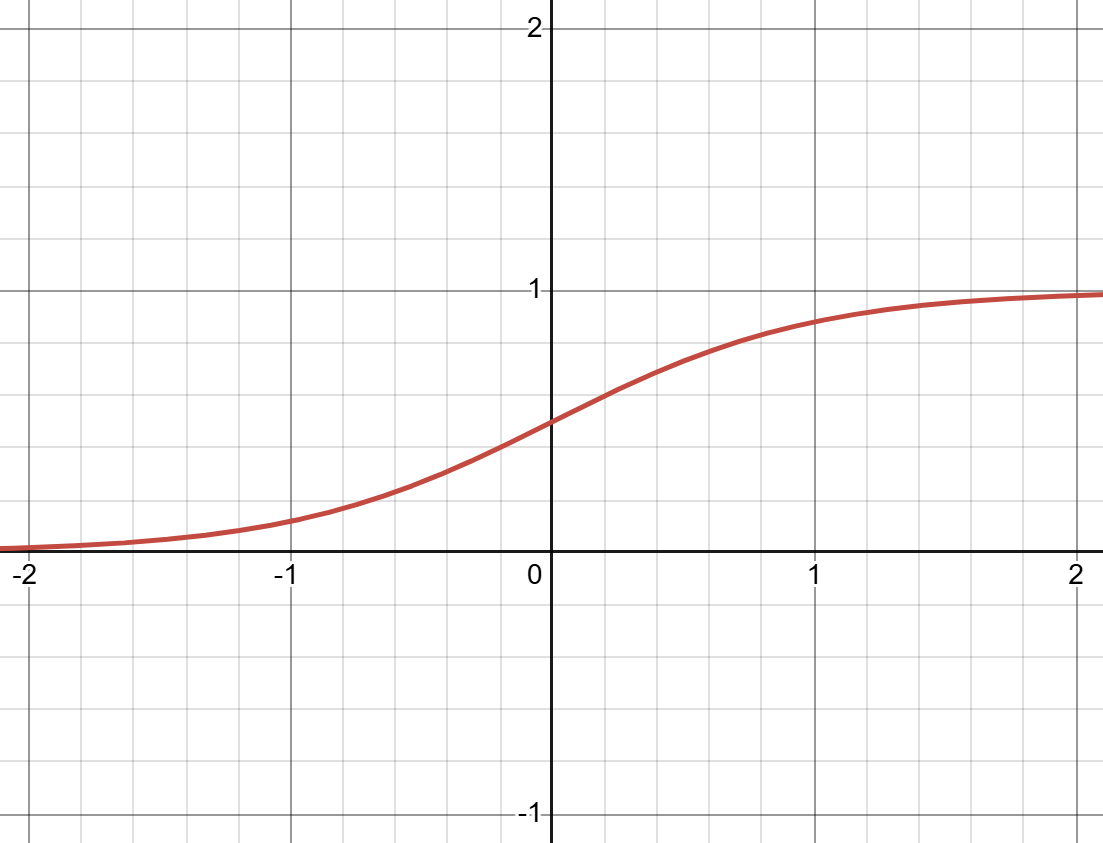
(H.Y. using Desmos)
Equation: \(\sigma(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}\), or \(tanh\) (hyperbolic tangent)
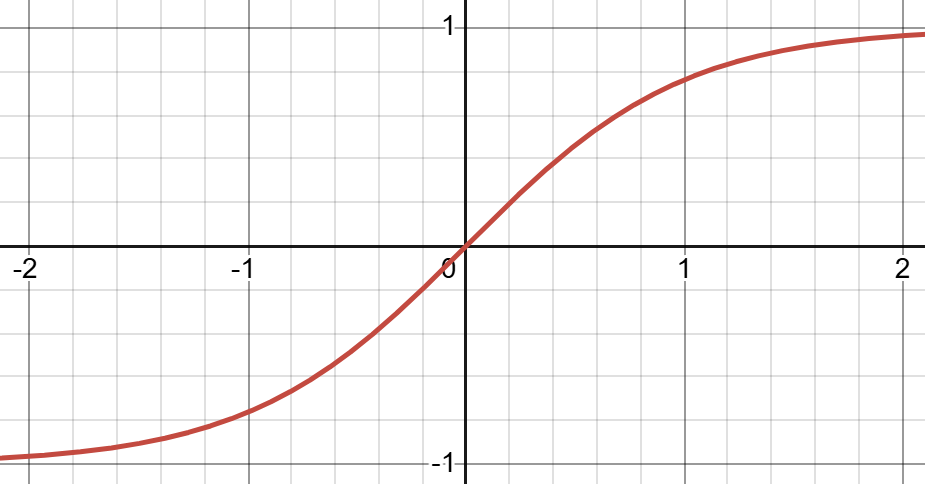
(H.Y. using Desmos)
Equation: \(f(x)=tanh(x)\). Then, we
normally randomly set all the parameters so that we can use backpropagation and gradient descent to minimise the cost function as best as possible.

PyTorch Logo (PyTorch, 2025)
In the past, this all had to be explicitly coded in complicated languages like C. However, modern software libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras make the implementation much easier by providing pre-defined layers, optimisers, and utilities for handling large datasets efficiently. If you would like to have a go at making a neural network yourself, here are some links and ideas for simple networks:
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Links & Tutorials:
- Medium Article by Mayur Ingole
- DataCamp Tutorial by Kurtis Pykes
- Machine Learning Mastery Article from Adrian Tam
- Kie Codes YouTube Video Tutorial
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Some Ideas for Easy-to Implement Neural Networks:
- Handwritten Digit Recogniser (Using the MNIST Dataset), ~60,000 handwritten digits with labels
- General Image Recogniser (Using the Google Open Images Dataset), ~9,000,000 images with bounding boxes & labels
- Disease X-Ray Recogniser (Using the NIH Chest X-ray Dataset), ~100,000 chest X-rays with disease labels
- Speech Recogniser (Using the LibriSpeech Dataset), ~1,000 hours of audiobook speech
- Clothing Classification Model (Using the Fashion-MNIST Dataset), ~70,000 clothing item images (same format as MNIST handwritten digits)
▬▬▬▬▬▬
8. Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks have now become one of the most influential technologies of all time, driving innovations that affect both our everyday experiences and cutting-edge scientific research.
By identifying patterns in vast amounts of data, neural networks can classify images, translate languages, predict outcomes and generate new content. And due to their flexibility and ability to adapt to new situations, neural networks can be used in a wide variety of fields, such as medicine, finance, robotics, and astronomy. The thing that makes neural networks so powerful and useful is their ability to "learn". Unlike traditional algorithms which have to be hard-coded, neural networks can improve their accuracy as they are exposed to more data, making them very important in today's digital age. Below are some of the most important areas where neural networks are used today:
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Virtual Assistants, Chatbots and Translators
Artificial neural networks also play an important role in natural language processing (NLP), where systems try to understand and process human language. From virtual assistants and chatbots like Siri or ChatGPT, to machine translation and summarisation, neural networks enable systems to generate and process text extremely efficiently. The latest models also utilise transformers and self-attention to better handle context, making them especially good for taks like question answering or sentiment analysis.
ChatGPT Logo (ChatGPT, 2025)
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Finance and Business
Neural networks are also often used for fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading. They can recognise patterns in transactions that might suggest fraudulent activity, or assess creditworthiness more accurately by looking at complex financial histories. Neural networks are also used by companies to predict customer behavior, advertising potential and demand, resulting in better, more relevant products and services.

AI in Business and Finance (Bernard Marr, n.d.)
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Healthcare and Medicine
In medicine, neural networks are used in diagnosis and treatment planning. They can analyse patient data to predict disease risk, assist with drug discovery, and recommend personalised therapies. Neural networks also
help with medical imaging, detecting subtle abnormalities that the human eye could miss. By integrating huge databases of patient history, neural networks are now extremely accurate in the detection of diseases at their earliest stage.
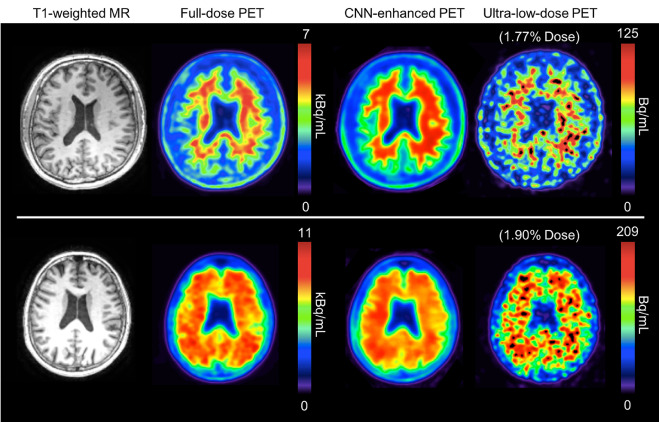
MRI Scan Enhancement with Neural Networks (ScienceDirect, 2021)
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Neural networks are also very commonly used in robotics and autonomous systems, where computer vision helps these systems perceive and interact with their environment. For example, autonomous vehicles use CNNs A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of neural network designed to process data with a grid-like structure, such as images. Instead of looking at the entire image at once, it uses small filters (kernels) that slide over the input to detect local patterns like edges, textures, or shapes, and then combines these to recognise more complex features. to detect obstacles, pedestrians and traffic signs, letting them operate more safely and efficiently. Manufacturing robots also use neural networks to help in tasks like visual inspection and machine assembly, where there is a need for flexibility and learning.
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Science and Research
Furthermore, neural networks are being used more and more today in science, engineering, mathematics and research. Because of their ability to analyse huge amounts of data effectively and predict outcomes accurately, neural networks, especially CNNsA Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of neural network designed to process data with a grid-like structure, such as images. Instead of looking at the entire image at once, it uses small filters (kernels) that slide over the input to detect local patterns like edges, textures, or shapes, and then combines these to recognise more complex features. and GANsA Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) consists of two competing neural networks: a generator that creates synthetic data and a discriminator that tries to distinguish between real and fake data. Through this adversarial training, GANs learn to produce highly realistic outputs, such as images, music, or even video., are used to simulate chemical interactions and biological processes, allowing for increased scientific discovery. Deep learning algorithms like Google DeepMind (AlphaEvolve) have also been able to prove mathematical theorems that have remained unsolved for hundreds of years. Thefore neural networks are used extensively in all STEM fields to accelerate scientific discoveries and innovation.
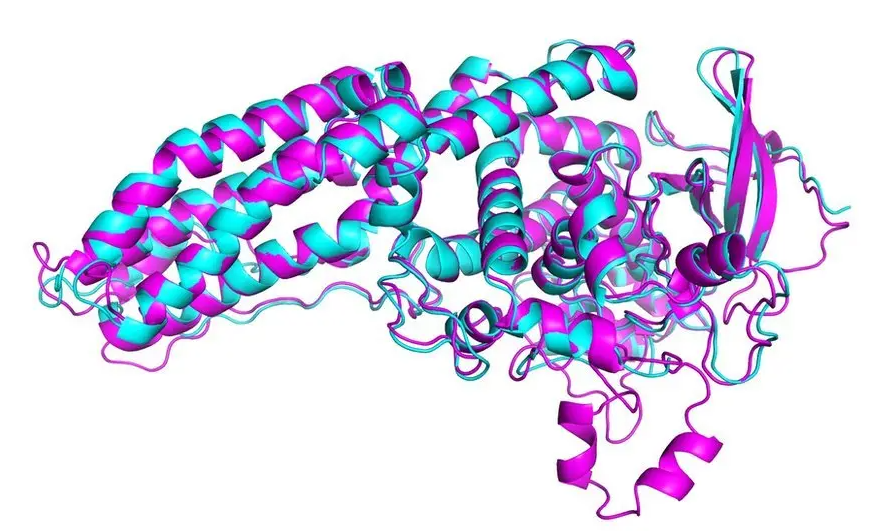
Protein Folding Predictions with AI (BBC, 2020)
For example, one of the most important problems in biology: predicting how proteins will fold in 3D, has been largely solved by AI. It is mostly the shape of the protein that determines what the protein can do and what functions it usually carries out, so being able to accurately predict these structures in 3D is very important. And, in 2020, a neural network model called AlphaFold determined the shape of around two thirds of the proteins with accuracy "comparable to laboratory experiments".
