Introduction to Neural Networks
Part 1
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field that encompasses a large number of different techniques for creating "intelligent" computer behavior, from decision trees and genetic algorithms, to probabilistic models and Bayesian networks. However, the Neural Network is arguably one of the most powerful and widely used of these methods.
▬▬▬▬▬▬
Essentially, a neural network is a system of interlinked nodesA node in a neural network is a small processing unit that takes input values, performs a simple calculation, and produces an output that helps the network make decisions or predictions. that learns data patterns in order to map inputs to the desired outputs. This makes it very useful for tasks that do not have clear rules that we can define, such as facial recognition, speech recognition, and generating human-like text.
Neural Networks are systems of interlinked nodes that learn data patterns in order to map inputs to the desired outputs
Neural networks were originally inspired by the human brain, which learns and adapts through billions of connected neurons. However, instead of biological neurons, neural networks use a set of digital "nodesA node in a neural network is a small processing unit that takes input values, performs a simple calculation, and produces an output that helps the network make decisions or predictions." arranged in different layers.

Neuron Diagram (Sora)
In most neural networks, there are 3 types of layers:
- The Input layer receives raw data (e.g. pixels, numbers, audio signals, etc.)
- The Hidden layers progressively transform the data, learning abstract features (e.g. edges → shapes → objects, or phonemes → words → meaning)
- The Output layer determines the final result, such as a classification, decision, or prediction
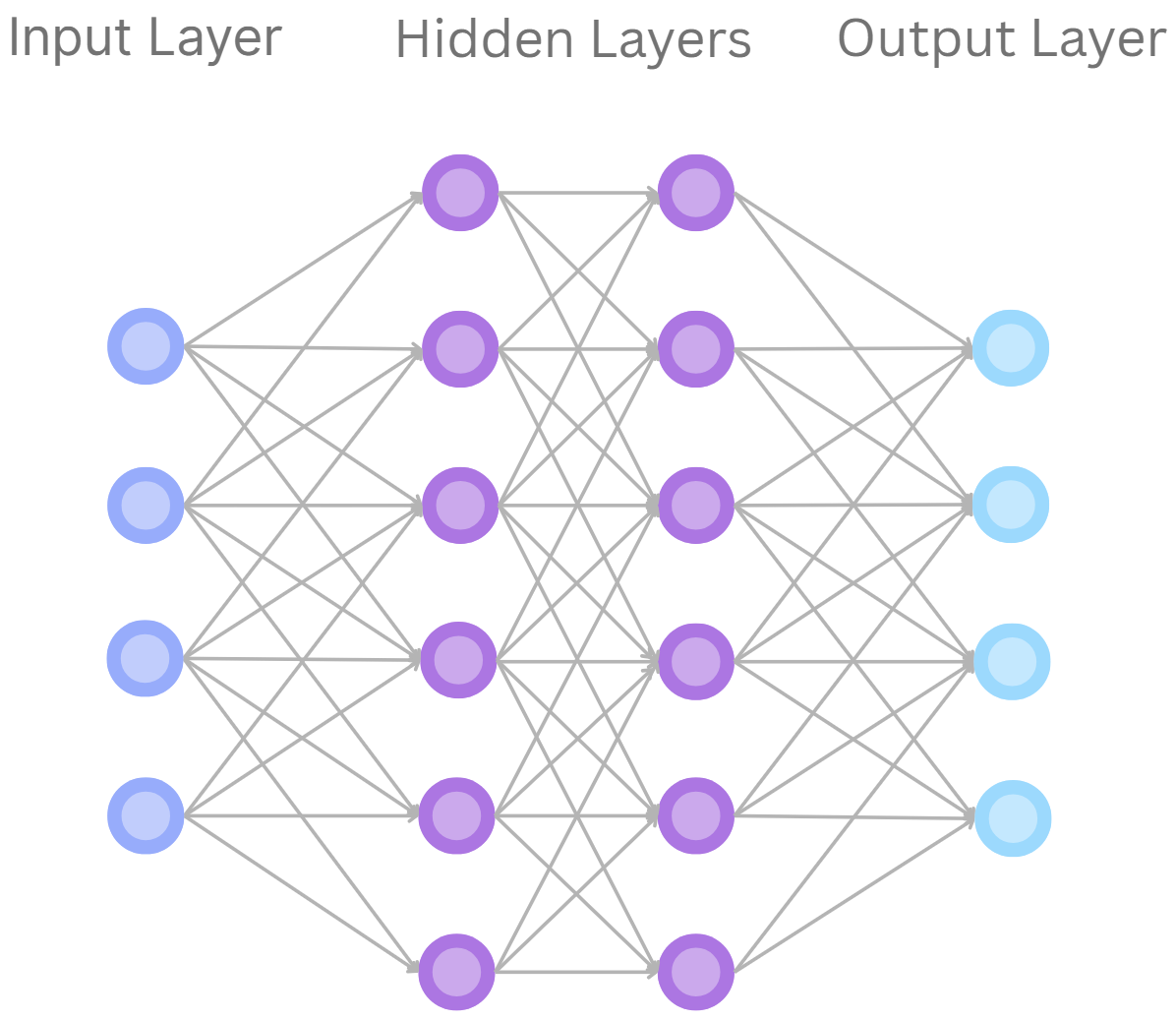
Neural Network Diagram (H.Y. using Canva)
What makes neural networks so powerful is that they improve over time. They learn from examples, compare their predictions with the actual answers, and modify themselves in order to give more accurate responses. Unlike traditional programming, where all rules must be specified beforehand, neural networks learn rules directly from real-life data.
Today, neural networks underpin the many modern AI systems and are causing innovation in areas such as computer vision, natural language understanding, and robotics.
